Massachusetts Commercial Roof Gutter Installation: Code Requirements and Best Practices
Reading Time: 5 minutes
Key Points about Commercial Gutters
- Research indicates that gutters on commercial roofs in Massachusetts can be installed externally if they meet material requirements.
- Codes do not mandate concealing gutters within the roof structure, but there are regulations for external placement.
- Consult local authorities to ensure you meet any potential additional requirements.
General Provisions for Commercial Gutters Installation in Massachusetts

Massachusetts building codes require that gutters and leaders installed on the exterior of commercial buildings (except for Group R-3, private garages, and Type V construction buildings) be made from noncombustible materials or Schedule 40 plastic pipe. This means that you can install external gutters, as long as you meet the specified material standards.
There is no explicit requirement to conceal gutters within the roof structure, allowing them to be placed externally if they are functional and safe. However, for some commercial buildings, particularly in historic districts, additional aesthetic or zoning regulations may apply, which should be verified with local authorities.
Installation Requirements According to Massachusetts Codes
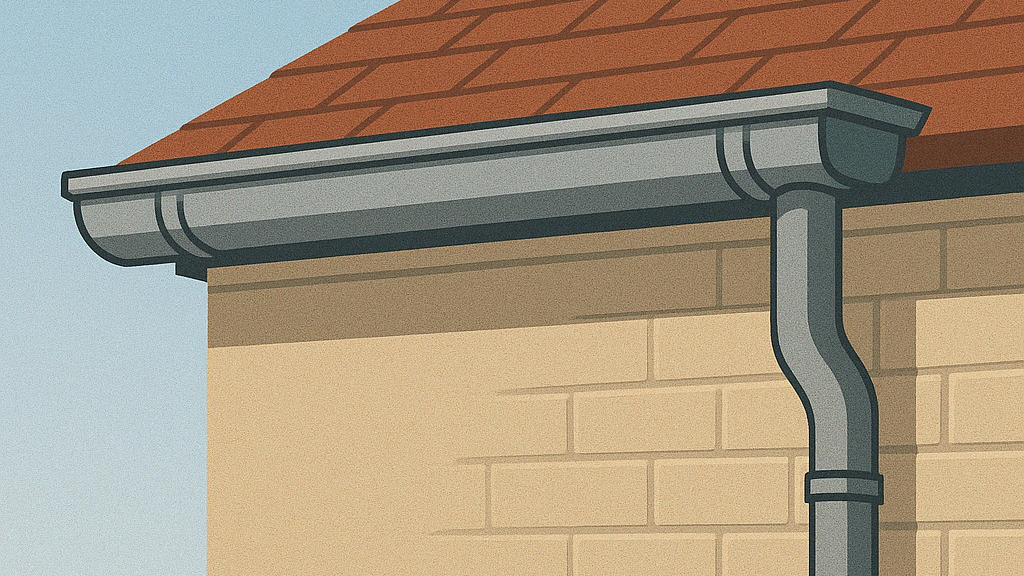
Codes such as 780 CMR (Massachusetts State Building Code) and 248 CMR (Uniform State Plumbing Code) regulate the installation of drainage systems, including gutters. Specifically, Section 1503.4.3 of 780 CMR states that externally placed gutters must be noncombustible or made of Schedule 40 plastic, confirming the allowance for external placement.
Allowance for External Commercial Gutters Placement
Research shows that gutters can be placed externally, as codes do not prohibit this and even provide requirements for external installations. The definition of “leaders” (downspouts) in 248 CMR as external drainage pipes for conveying water from roofs or gutters further supports this possibility.
Requirement to Conceal Within the Roof
There is no mandatory requirement to conceal gutters within the roof structure for commercial buildings. Codes focus on functionality and safety rather than aesthetics, unless local regulations specify otherwise.
Report: Detailed Analysis of Commercial Gutters Installation Rules for Commercial Roofs in Massachusetts

This report provides a comprehensive overview of the rules for installing gutters on commercial roofs in Massachusetts, based on current building and plumbing codes, such as 780 CMR (Massachusetts State Building Code) and 248 CMR (Uniform State Plumbing Code). The analysis addresses proper installation according to codes, the possibility of external gutter placement, and the necessity of concealing gutters within the roof structure.
Context and Legal Framework
The Massachusetts State Building Code (780 CMR) is based on the 2021 International Building Code (IBC) with amendments adopted by the Board of Building Regulations and Standards (BBRS). The tenth edition of 780 CMR, effective October 11, 2024, operates concurrently with the ninth edition until June 30, 2025. For commercial buildings, the base volume applies, covering all structures not governed by residential codes.
Plumbing aspects, including drainage systems, are regulated by 248 CMR 10.00, the Uniform State Plumbing Code, effective December 8, 2023. This code governs the installation, alteration, removal, replacement, repair, or construction of all plumbing systems, including stormwater and drainage systems.
Definitions and Materials about Commercial Gutters
Key definitions from 248 CMR 10.03 include:
- Roof Drain: A receptor installed to collect water from a roof surface and convey it to a drainpipe or collector.
- Leader: An exterior drainage pipe for conveying stormwater from roofs or gutters.
- Storm Drainage System: A system that transports rainwater, surface water, condensate, cooling water, or similar clean liquid wastes to a storm sewer or other disposal location, excluding sewage or industrial wastes.
Materials for drainage systems, specified in 248 CMR 10.06, include cast iron, copper, steel, and plastic pipes meeting standards for underground and aboveground installations. For example, aboveground systems may use galvanized steel pipes no lighter than Schedule 40 and epoxy fiberglass systems for stormwater.
Installation Requirements According to Codes
Section 1503.4.3 of 780 CMR directly regulates gutters:
- “Gutters and leaders placed on the exterior of buildings, other than Group R-3, private garages, and buildings of Type V construction, shall be of noncombustible material or Schedule 40 plastic pipe.” This indicates that for commercial buildings (not R-3 or Type V), external gutter installation is permitted, provided material compliance is met. Group R-3 pertains to residential buildings such as one- and two-family dwellings and townhouses, while Type V refers to wood-frame constructions, often used for residential buildings. Thus, commercial buildings generally fall under this requirement.
Section 10.17 of 248 CMR regulates stormwater, including system sizing based on the maximum surface area to be drained, per Table 1 (sizing of horizontal stormwater drains). An exception is made for siphonic roof drainage systems, where design responsibility lies with a Massachusetts-licensed engineer, ensuring compliance with sizing and functionality.
Allowance for External Gutter Placement
Codes explicitly permit external gutter placement, as stated in 780 CMR 1503.4.3, which refers to “gutters and leaders placed on the exterior of buildings.” The definition of a leader as an exterior drainage pipe in 248 CMR 10.03 further confirms that gutters may be installed externally, meeting functional drainage requirements.
There is no indication that gutters must be concealed within the roof structure, allowing architects and builders to opt for external installation if it complies with safety and efficiency standards.
Requirement to Conceal Within the Roof

Codes do not mandate concealing gutters within the roof structure for commercial buildings. The focus is on functionality, safety, and material compliance, not aesthetics, unless local zoning or historic regulations dictate otherwise. For example, historic districts may impose additional aesthetic requirements, but these are outside the scope of general building codes and require consultation with local authorities.
Additional Considerations
While codes do not prohibit external installation, local conditions, such as heavy rainfall or snowfall, should be considered. For instance, areas with intense precipitation may require additional measures to prevent system overload. Additionally, aesthetic considerations may influence the choice between visible and concealed systems in some cases, but this is not reflected in the codes.
Key Gutter Requirements
| Aspect | Requirement | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Materials for External Gutters | Noncombustible materials or Schedule 40 plastic | Applies to commercial buildings, not R-3 or Type V |
| Placement | Can be external if compliant with codes | No requirement to conceal within roof |
| Siphonic System Design | Responsibility of a Massachusetts-licensed engineer | Specified in 248 CMR 10.17 |
| Local Regulations | Possible additional aesthetic requirements in historic districts | Requires consultation with local authorities |
Key Takeaways for Gutter Installation in Massachusetts
Research indicates that gutters on commercial roofs in Massachusetts can be installed externally if they meet material requirements specified in 780 CMR 1503.4.3. There is no mandatory requirement to conceal them within the roof structure, providing design flexibility, provided functional and safety standards are met. It is recommended to consider potential local zoning or historic regulations that may affect aesthetics and to consult with local authorities for clarification.
Key Sources
- 780 CMR: Amendments to the 2021 International Building Code, Chapter 15, Section 1502.4
- 248 CMR 10.00: Massachusetts Uniform State Plumbing Code, Section 10.03, Definitions
- 248 CMR 10.00: Massachusetts Uniform State Plumbing Code, Section 10.17, Storm Drains
- Massachusetts State Building Code, 780 CMR, Tenth Edition, Effective October 11, 2024
- Massachusetts Uniform State Plumbing Code, 248 CMR 10.00, Effective December 8, 2023
Denis is the driving force behind ID Flat Roof, a leading company in Boston specializing in flat roof repair and installation for over 20 years.
Expertise:
Denis excels in PVC, TPO, EPDM, and rubber roofing. His meticulous approach ensures quality and customer satisfaction.
Innovation:
Denis incorporates cutting-edge solutions like skylights and solar PV roofing.